What negative impact is the Three Gorges Dam having on the environment?
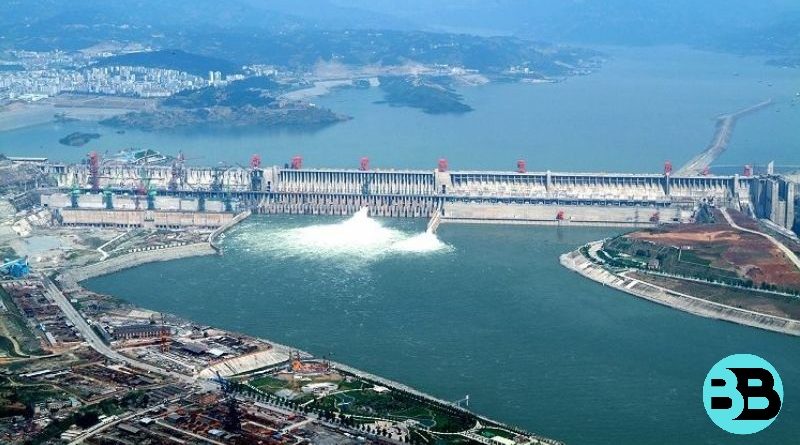
The Three Gorges Dam, located on the Yangtze River in China, is one of the largest hydropower projects in the world. While it has brought numerous benefits to the region, including flood control, power generation, and improved navigation, it has also had significant negative impacts on the environment.
One of the most significant environmental concerns associated with the Three Gorges Dam is the displacement of people and the destruction of ecosystems. To construct the dam, more than 1.3 million people were displaced from their homes, farms, and communities. This mass resettlement has caused immense social and psychological upheaval for the affected population. Moreover, the flooding of the reservoir has led to the loss of fertile agricultural land and the destruction of natural habitats, resulting in the loss of biodiversity.
The dam has also disrupted the natural flow of the Yangtze River, leading to a range of ecological consequences. The altered water levels and reduced sediment transport have affected the river’s ecology downstream, including the estuary and the East China Sea. The reduced sediment flow has resulted in erosion of the riverbanks and coastal areas, threatening infrastructure and coastal ecosystems. Additionally, the dam has hindered the migration of fish species, impacting both the commercial fishing industry and the biodiversity of the river system.
Another significant concern is the increased risk of landslides and earthquakes caused by the dam. The large reservoir created by the dam puts immense pressure on the surrounding geological structures, leading to an increased likelihood of landslides. This has already resulted in several landslide incidents in the region, causing loss of life and property. Additionally, the weight of the water in the reservoir has the potential to trigger seismic activity, increasing the risk of earthquakes in the area. These geological hazards pose a threat to both human settlements and the natural environment.
Furthermore, the construction and operation of the Three Gorges Dam have had negative implications for water quality and pollution. The accumulation of stagnant water in the reservoir has facilitated the growth of algae blooms, leading to eutrophication. These blooms deplete oxygen levels in the water, suffocating aquatic life and disrupting the ecological balance. The dam has also trapped pollutants and sediment, resulting in the accumulation of heavy metals and other toxins in the reservoir, which can be harmful to both human and aquatic life.
The dam has had a profound impact on the river’s hydrological regime, altering the seasonal water flows. The regulation of water levels throughout the year has disrupted the natural flood cycles that play a vital role in the river’s ecosystem. Floodwaters usually replenish wetlands, flush out pollutants, and transport sediment downstream, but the dam has significantly reduced these processes. As a result, the downstream ecosystem has been deprived of these essential functions, leading to ecological imbalance and degradation.
Moreover, the construction and operation of the dam have contributed to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. The flooding of large areas of land for the reservoir has led to the decomposition of submerged vegetation, releasing significant amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Methane emissions from the reservoir contribute to global warming and exacerbate climate change impacts. Additionally, the construction process itself, involving the use of heavy machinery and the extraction of construction materials, has resulted in carbon emissions.
The dam’s presence has also disrupted the natural sediment transport along the Yangtze River. The dam traps sediment upstream, leading to the loss of sediment downstream. This loss of sediment affects the replenishment of the river delta and coastal areas, which rely on the influx of sediment for their stability and sustainability. The reduced sediment supply can accelerate coastal erosion, increase the vulnerability of coastal communities to flooding and storm surges, and adversely impact estuarine and marine ecosystems.
Furthermore, the dam has had socio-economic implications, indirectly impacting the environment. The construction of the Three Gorges Dam required significant amounts of materials, including concrete, steel, and other resources. The extraction and transportation of these materials have resulted in habitat destruction, deforestation, and increased carbon emissions. Additionally, the dam’s reservoir has altered the local climate, leading to changes in temperature and humidity, which can have cascading effects on agricultural productivity and local ecosystems.
The dam has also disrupted the natural flow of sediment and nutrients downstream, affecting the productivity of agricultural lands and fisheries. The reduced sediment flow, coupled with the dam’s regulation of water levels, has altered the floodplain dynamics and nutrient distribution in the region. As a result, agricultural lands that once relied on natural flooding for nutrient replenishment now require additional inputs of fertilizers, leading to increased costs and potential water pollution. Similarly, the reduced nutrient flow downstream has impacted fish populations and the livelihoods of communities dependent on fishing.
Furthermore, the Three Gorges Dam has caused changes in water temperature and oxygen levels in the reservoir, which have negative implications for aquatic ecosystems. The dam releases water from the bottom of the reservoir, which is colder and depleted of oxygen. This can have adverse effects on fish species that require specific temperature ranges and oxygen levels for survival and reproduction. The altered thermal and oxygen regimes in the reservoir can result in the decline of certain fish species and disrupt the overall balance of the aquatic ecosystem.
In addition to the immediate environmental impacts, the long-term sustainability of the Three Gorges Dam is also a concern. The dam is subjected to the accumulation of sediment in the reservoir, which reduces its storage capacity over time. As sediment builds up, the dam’s effectiveness in flood control diminishes, necessitating costly dredging operations. Moreover, the structure itself is vulnerable to the effects of aging, erosion, and sedimentation, which could lead to structural integrity issues and potential risks to downstream communities.
In response to the negative environmental impacts of the Three Gorges Dam, the Chinese government has implemented measures to mitigate some of the issues. These include initiatives to reduce pollution, enhance biodiversity conservation, and improve fish migration through the construction of fish ladders and fish-breeding centers. However, the effectiveness of these measures remains a subject of debate, and their ability to restore the natural balance and functionality of the ecosystem is uncertain.
In conclusion, while the Three Gorges Dam has brought notable benefits in terms of flood control, power generation, and navigation, it has also had significant negative impacts on the environment. The displacement of people, destruction of ecosystems, disruption of natural flow patterns, increased risk of landslides and earthquakes, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions are among the adverse effects associated with the dam. These environmental concerns have wide-ranging implications for biodiversity, aquatic ecosystems, climate change, and the socio-economic well-being of communities in the region. It is crucial to continue monitoring and evaluating the environmental impacts of large-scale infrastructure projects like the Three Gorges Dam and strive to find sustainable solutions that balance the benefits and risks to both human populations and the natural environment.
Read also:
China’s Three Gorges Dam: An Environmental Catastrophe?





You truly did more than visitors’ expectations. Thank you for rendering these helpful, trusted, edifying and also cool thoughts on the topic to Kate.
I’ve bookmarked your site, and I’m adding your RSS feeds to my Google account.