Effects of Dams on the Environment
Introduction:
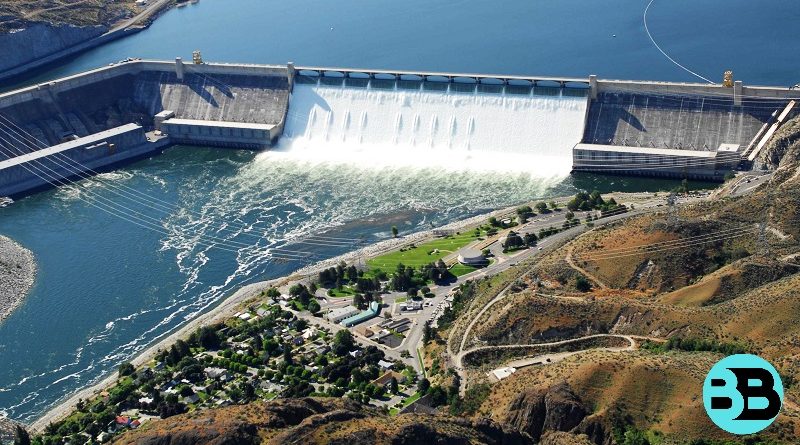
Dams are man-made structures that are built across rivers and other water bodies to create reservoirs that store water. The primary purpose of building dams is to provide a steady supply of water for irrigation, drinking, and other domestic purposes. Dams also generate hydroelectric power, which is a clean and renewable source of energy. However, the construction and operation of dams can have significant environmental impacts that can have far-reaching consequences. In this essay, we will discuss the effects of dams on the environment.
Alteration of river flows:
One of the most significant effects of dams on the environment is the alteration of river flows. When a dam is constructed, it creates a reservoir that can store water for long periods. This can significantly reduce the flow of water downstream of the dam, which can have several adverse effects. For example, it can alter the natural hydrological cycle of the river, affecting the ecosystem of the area. It can also lead to the loss of aquatic habitats, including wetlands and riparian zones.
Loss of aquatic habitats:
The creation of reservoirs by dams can result in the loss of aquatic habitats. The flooding of the areas upstream of the dam can destroy wetlands and other habitats that support aquatic plants and animals. The reduction in water flow downstream of the dam can also result in the loss of habitats, as some aquatic species may not be able to survive in the altered conditions. The loss of aquatic habitats can have a significant impact on the biodiversity of the area, as many species are dependent on these habitats for their survival.
Changes in water quality:
The construction and operation of dams can also have an impact on water quality. The accumulation of sediment in the reservoir can reduce the water’s quality, making it less suitable for drinking and irrigation. The stagnation of water in the reservoir can also lead to the growth of algae and other microorganisms, which can affect water quality. The discharge of water from the dam can also affect downstream water quality, as it can alter the temperature, dissolved oxygen levels, and nutrient content of the water. These changes can have a significant impact on aquatic ecosystems, as many species are sensitive to changes in water quality.
Disruption of fish migration:
Many fish species migrate upstream to spawn, and the construction of dams can disrupt this migration. Fish are not able to swim up and over the dam, and as a result, their natural habitat is altered. This can have a significant impact on fish populations, as it can reduce their breeding success and survival rates. In some cases, fish ladders or other fish passage facilities may be installed to help fish navigate around the dam, but these facilities are not always effective.
Soil erosion and sedimentation:
The construction and operation of dams can lead to soil erosion and sedimentation. When a river is dammed, sediment accumulates in the reservoir upstream of the dam, which can reduce the capacity of the reservoir and affect water quality. The reduced sediment flow downstream of the dam can also cause erosion of the riverbanks and streambeds, leading to habitat loss and changes in the landscape. Soil erosion and sedimentation can have significant impacts on the ecosystem of the area, as it can affect the health of plants and animals that depend on the river.
Climate change impacts:
Dams can also have an impact on climate change. The creation of reservoirs can result in the release of greenhouse gases, such as methane, which are produced when organic matter decomposes in the water. The generation of hydroelectric power by dams is also considered a clean and renewable source of energy, but the construction and operation of dams can have significant carbon footprints. Additionally, changes in river flows and water temperature can affect the climate in the area, as well as the ecosystem.
Societal impacts:
The construction and operation of dams have significant impacts on local communities. The displacement of people from their homes and land to make way for the reservoir can have social and economic impacts. Many communities that rely on fishing or farming may be negatively impacted by changes in water flows or water quality. The loss of cultural and historical sites due to flooding can also have significant impacts on communities. In some cases, the benefits of the dam may not outweigh the social and economic costs to local communities.
Conclusion:
The construction and operation of dams can have significant environmental impacts that can affect ecosystems, water quality, and local communities. The alteration of river flows, loss of aquatic habitats, changes in water quality, disruption of fish migration, soil erosion and sedimentation, climate change impacts, and societal impacts are just some of the many effects of dams on the environment. While dams can provide important benefits, such as a steady supply of water and renewable energy, it is essential to carefully consider the environmental and social costs of building and operating dams. It is important to develop sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions that balance the needs of human societies and the natural world.
Read also:
Environmental Impacts of Dams